The ACT Government has contracted large-scale renewable energy projects to supply electricity.
Each project sells its electricity in the National Energy Market at the price set by the market at half-hourly intervals.
If that price is greater than the contracted price, the generator pays the excess to the ACT Government. If the price is less than the contracted price, the ACT Government pays the difference to the generator.
The ACT Government relies on Evoenergy for a number of electricity supply functions.
One of those is to purchase wholesale electricity from the National Energy Market for ACT consumers.
Another is to pay or receive amounts for contracted large-scale renewable energy projects each quarter.
Evoenergy recently requested an increase in the price it charges for wholesale electricity to the ACT because, it said, payments for the ACT Government large-scale renewable energy generators had increased.
“Over the past year, there has been a significant drop in wholesale electricity prices making them much lower than the contract prices the ACT Government established with large-scale generators. This has resulted in significant top-up payments required to cover the difference,” said Evoenergy’s General Manager Peter Billing.
“We understand it can be confusing when wholesale prices are going down and these costs have gone up. The reality is these costs are fixed by contracts whereas the electricity market and the wholesale electricity price moves based on supply and demand.”
“Evoenergy has no control over the long-term contracts with renewable energy generators or the resulting top up payments, however we will continue to work with the ACT Government as part of our legislated responsibility to administer the large-scale feed-in tariff scheme.”
The statement "we understand it can be confusing" is quite precise.
The wholesale price at which Evoenergy purchases electricity for ACT consumers has fallen sharply.
The amount Evoenergy pays for contract prices for ACT Government large-scale generators has risen for the same reason.
Evoenergy has made no attempt to explain why the savings in its wholesale electricity purchases have not offset the resulting increase in payments for ACT Government large-scale generators.
If it has failed to achieve this offset, then its purchase strategy needs to be reviewed and responses put in place to address this.
The second quarter of 2019-2020 (October to December 2019) and of 2020-2021 (October to December 2020) illustrate why it is confusing for Evoenergy to "explain" an increase in its electricity charges that ignores the decrease in the price of electricity it purchases...
In each of the above quarters, the ACT Government contracted large-scale renewable energy generators sold about 500,000 megawatt-hours of electricity.
In October to December 2019 the renewable energy generators received $27.4 million from the National Energy Market. Evoenergy paid the generators $18.7 million under the ACT Government contracts with them.
A year later, in October to December 2020 the renewable energy generators received just $13.8 million from the National Energy Market. Due to that decrease, Evoenergy paid the generators $30.8 million under the ACT Government contracts with them.
THE NET CHANGE IS A POTENTIAL SAVING OF $1.5 MILLION BY EVOENERGY.
Evoenergy's payments for the ACT Government contracts increased by $12.1 million (from $18.7 to $30.8 million) - but only because the electricity it and other wholesale electricity purchasers paid via the National Energy Market decreased by $13.6 million (from $27.4 to $13.8 million).
The following charts illustrate that as the National Energy Market price changes - from day to day - the offsetting payments under the ACT Government large-scale renewable energy contracts vary by an identical but opposite amount. The result is a fairly constant cost - that Evoenergy should aim to achieve - of about $90 per MWh.
 |
| AEMO Price per MWh and ACT Government Payment per MWh - 2nd Quarter 2019-2020 |
 |
| AEMO Price per MWh and ACT Government Payment per MWh - 2nd Quarter 2020-2021 |
The price of electricity the renewable energy projects received in the average of each half hour of all the days from October to December 2019, and from October to December 2020, show a consistent and steep fall in 2020.
This fall reflects the reduction in the cost of wholesale electricity Evoenergy purchases for supply to ACT busnesses and homes.
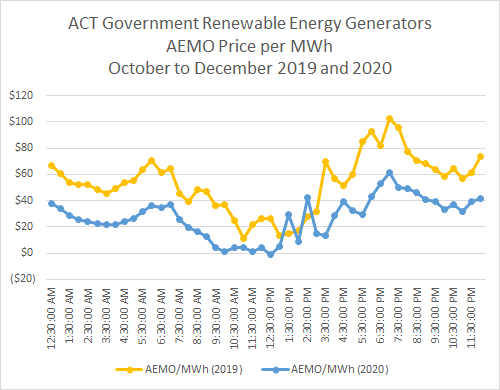 |
| AEMO average price per MWh in each half hour for ACT renewable energy generators |
